Docker Containers and Images
Commands
|
|
Overview
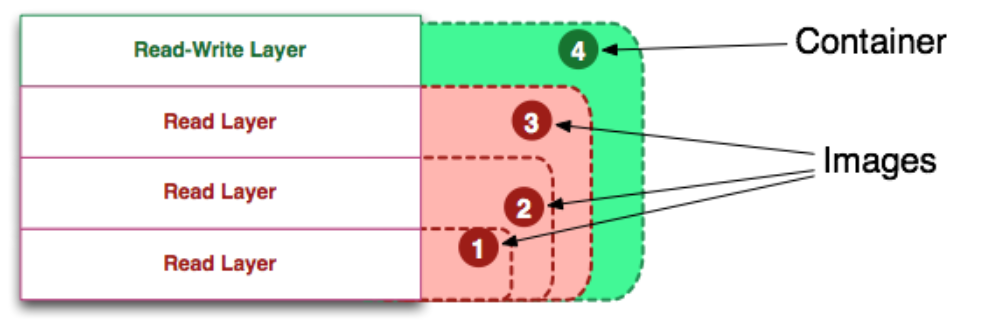
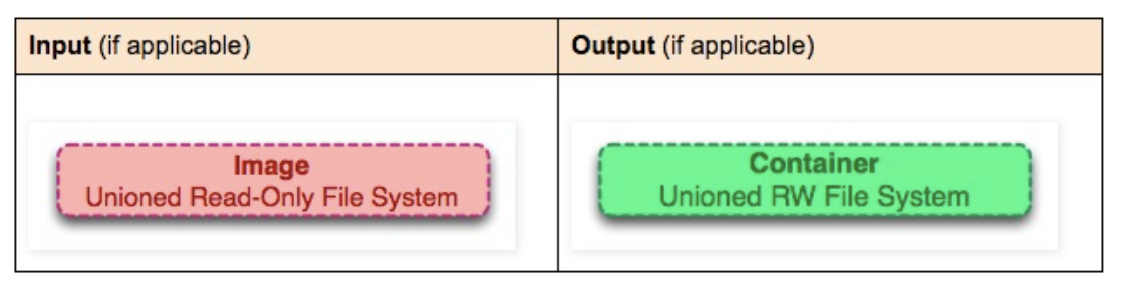
As shown in the figure, images are read-only layers, while containers are read-write layers.
Definitions
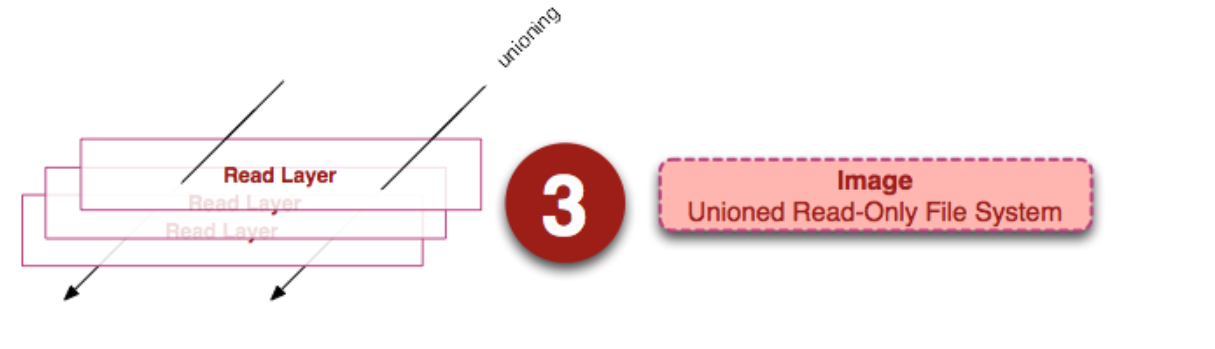
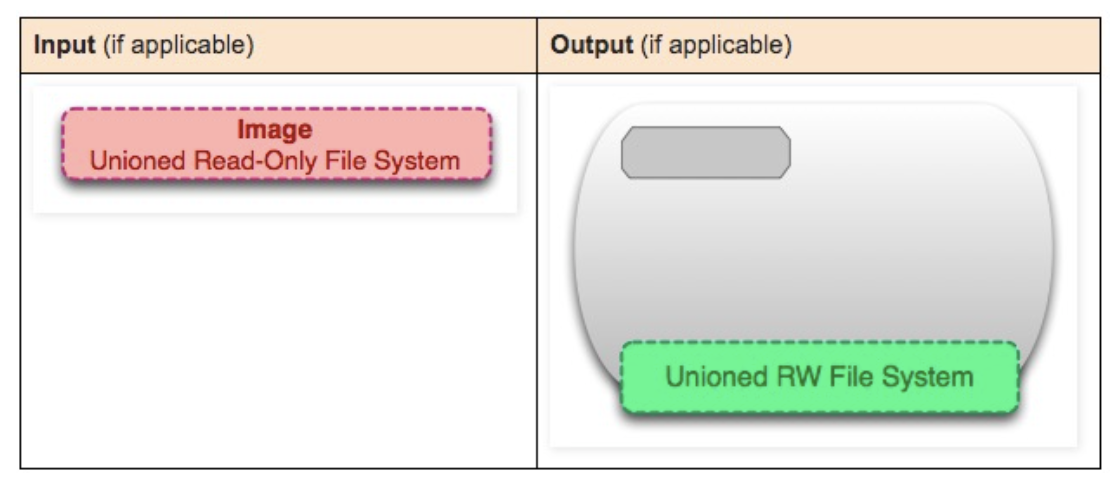
Image
An image is a unified view of a stack of read-only layers. Except for the bottom layer, all other layers have a pointer to the next layer. From the user’s perspective, this is a unified file system.
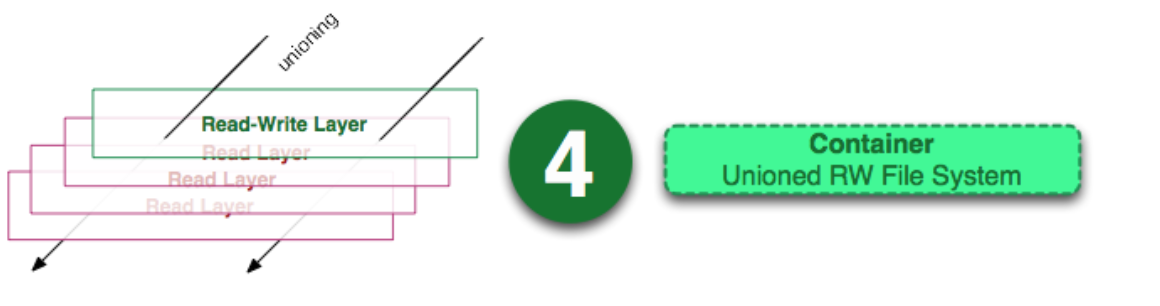
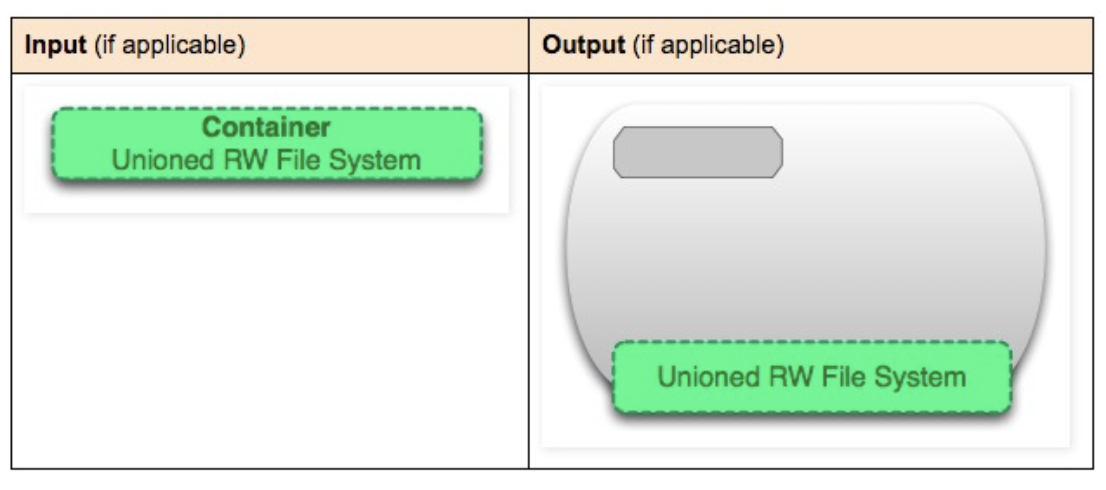
Container
Container = Image + Read-write layer. The definition of a container does not mention whether the container needs to be running.
Running Container
Running Container = Container + Isolated process space + Processes.
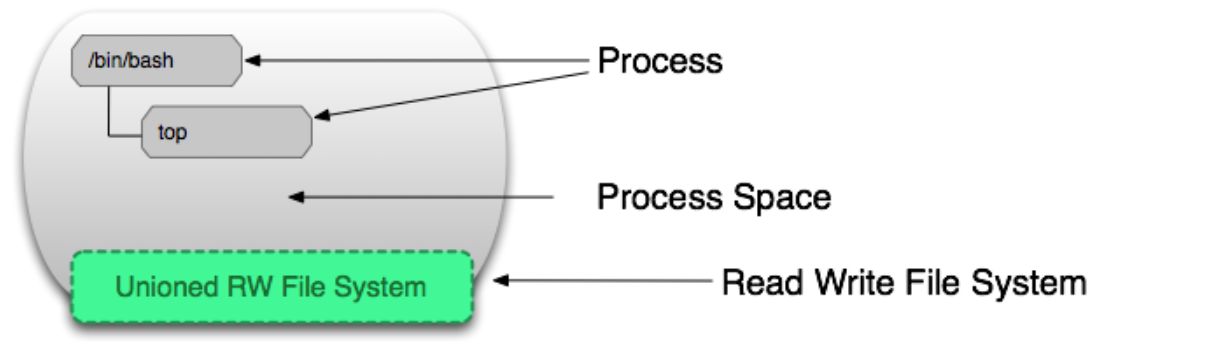
As shown below, the behavior of processes in a container acts on the read-write layer.
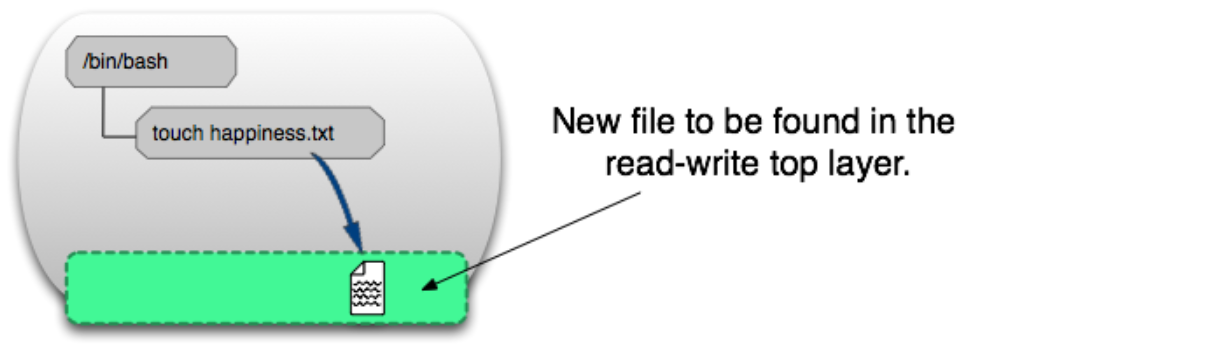
Image Layer
Understanding with Commands
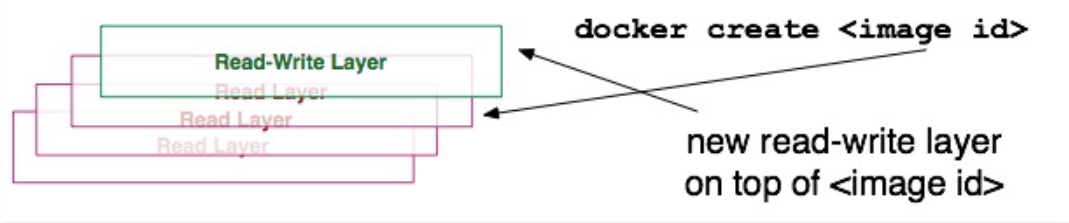
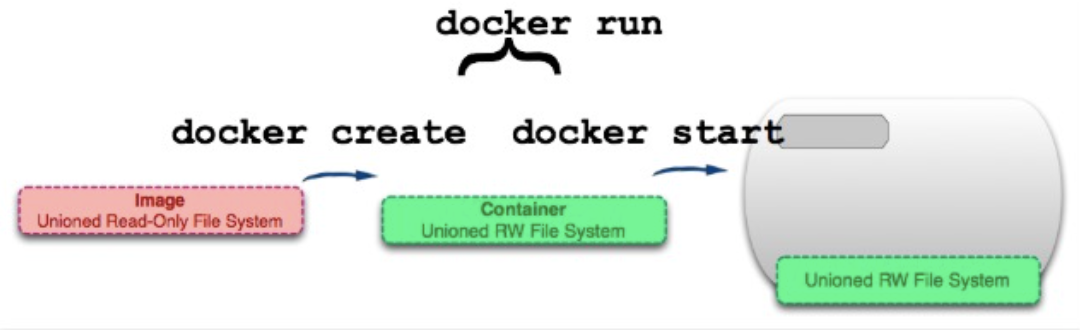
docker create image-id
Add a read-write layer to an image to form a container. The container is not running after creation.
docker start container-id
Create a process isolation space for the container.
docker run image-id
run = create + start
docker ps
List running containers
docker ps –a
List all containers
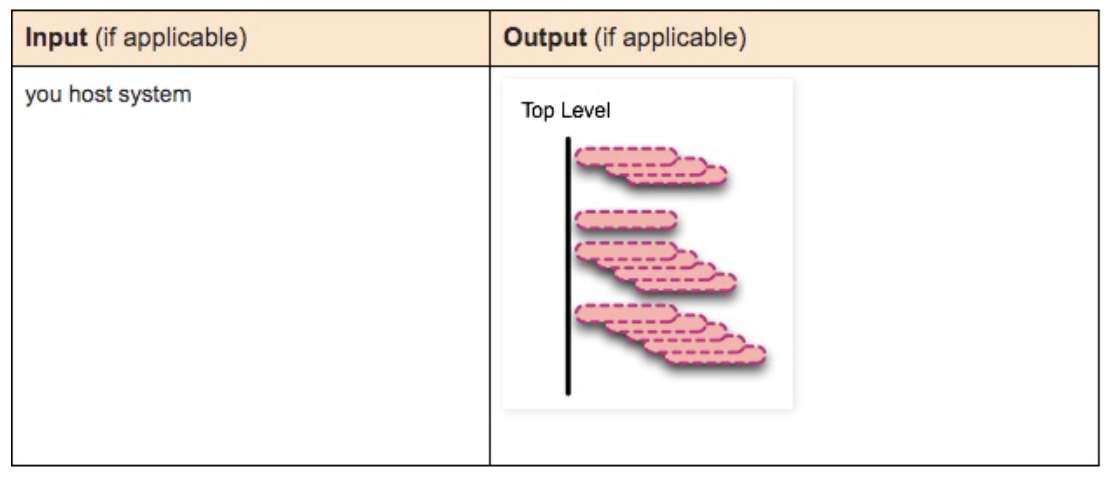
docker images
List all top-level images. Top-level images refer to images used to create containers or images that can be pulled directly.
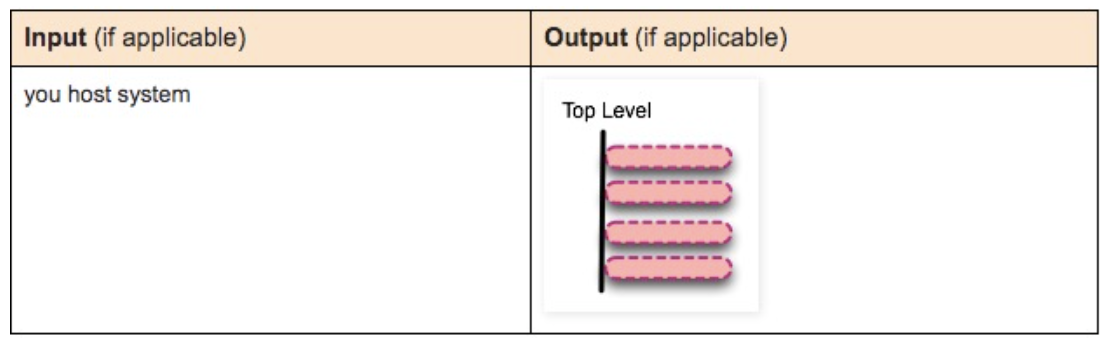
docker images –a
List all images.
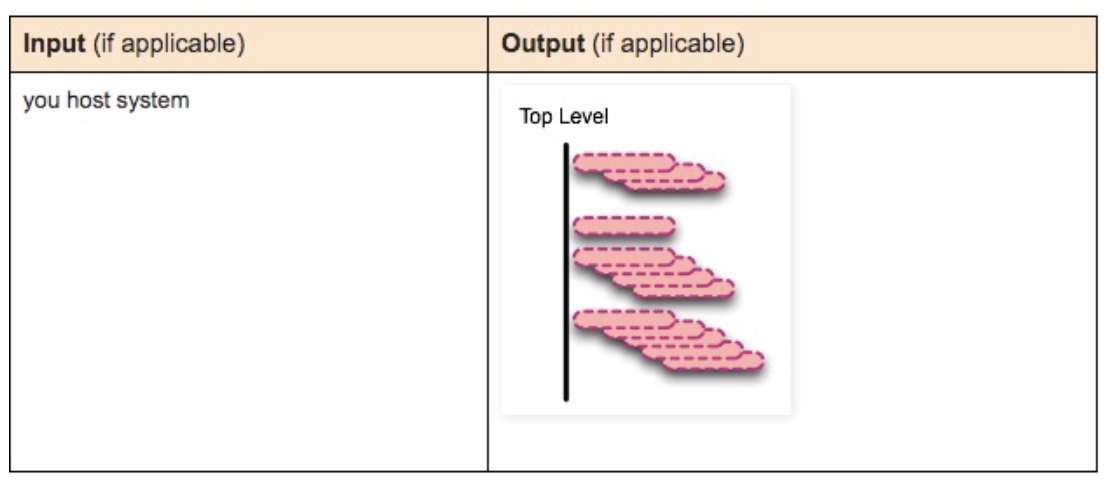
docker stop container-id
Send SIGTERM signal to stop all processes in the running container.
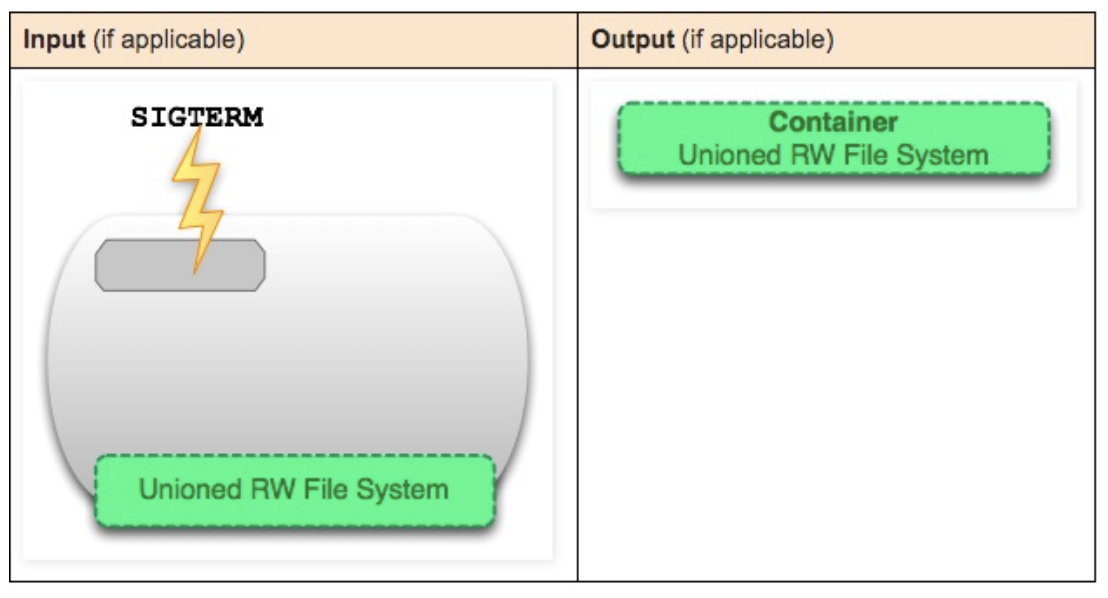
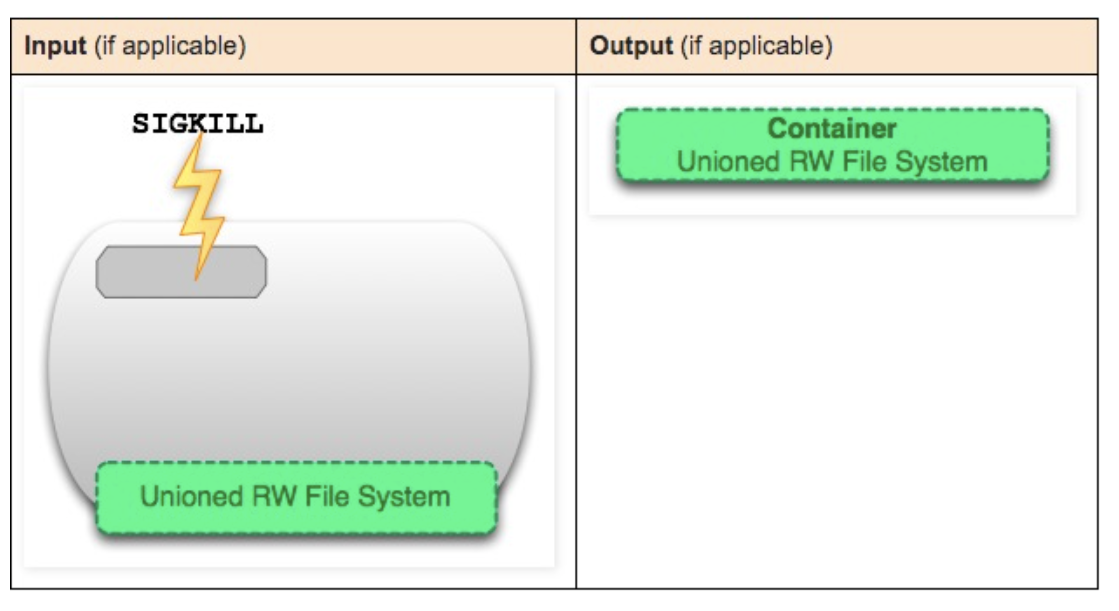
docker kill container-id
Send SIGKILL signal to stop all processes in the running container.
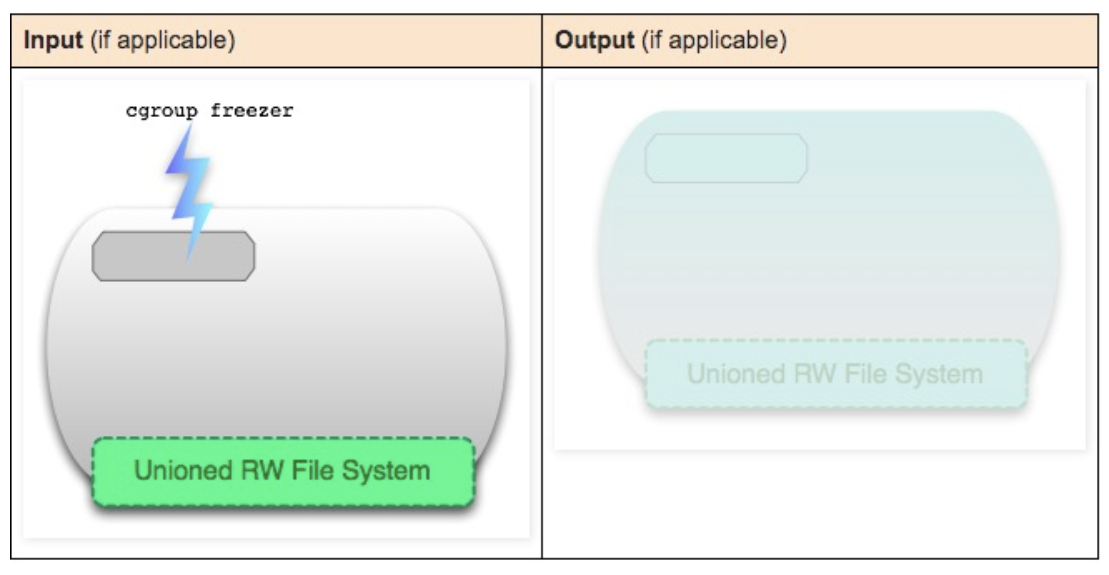
docker pause container-id
Pause all processes in the container using cgroups freezer. Sends SIGTSTP signal.
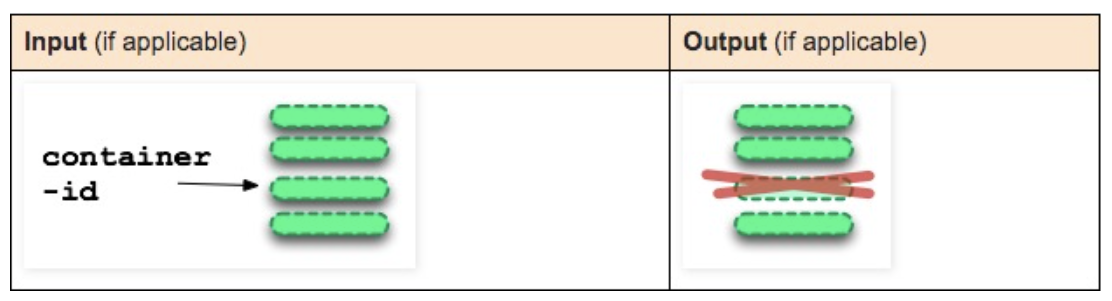
docker rm container-id
Remove the read-write layer (container).
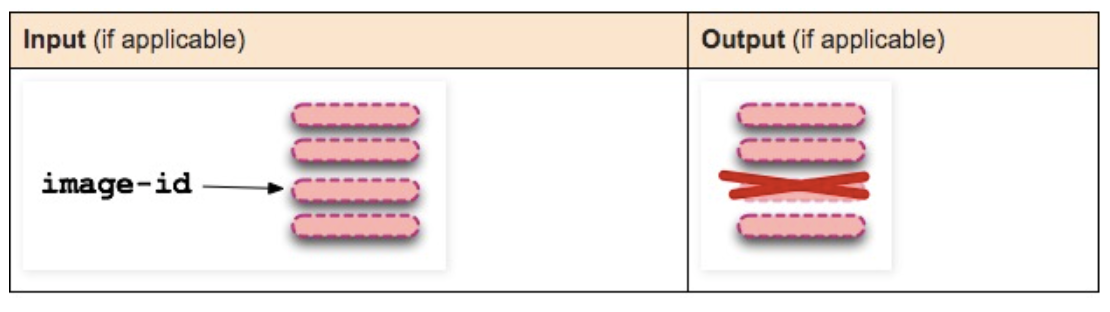
docker rmi image-id
Remove image.
OPTIONS description:
- -f: Force deletion;
- –no-prune: Do not remove intermediate images of this image, remove by default;
When the same image has multiple tags, executing the docker rmi command only deletes the specified tag from the image’s many tags and does not affect the original image file. If an image does not have multiple tags, and there is only one tag, be careful when executing the delete command, as this will completely delete all file layers of the image.
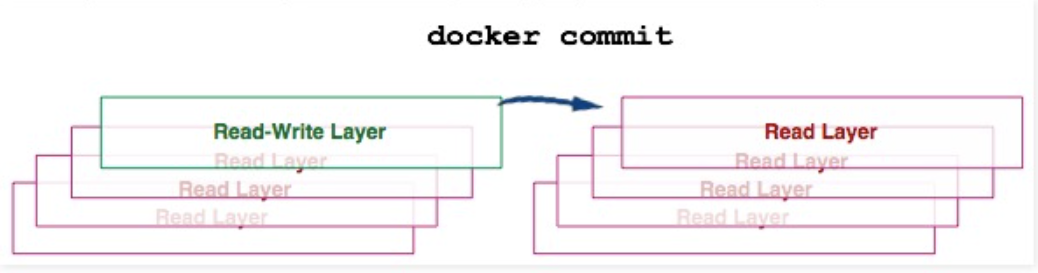
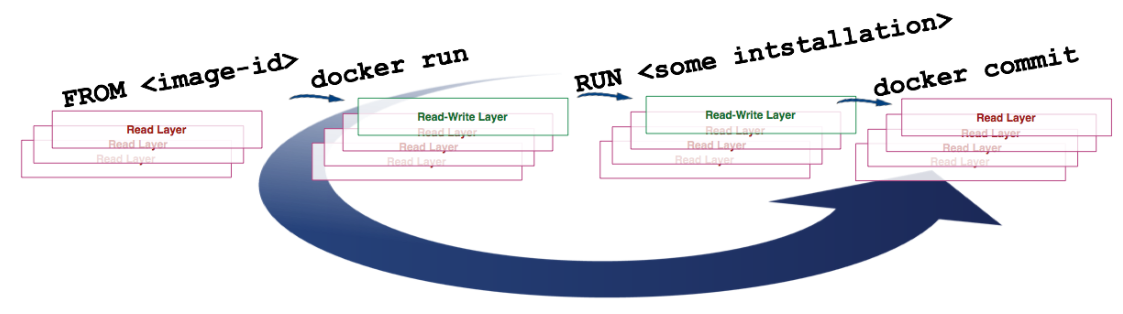
docker commit container-id
Convert the container’s read-write layer to a read-only layer, transforming the container into an image.

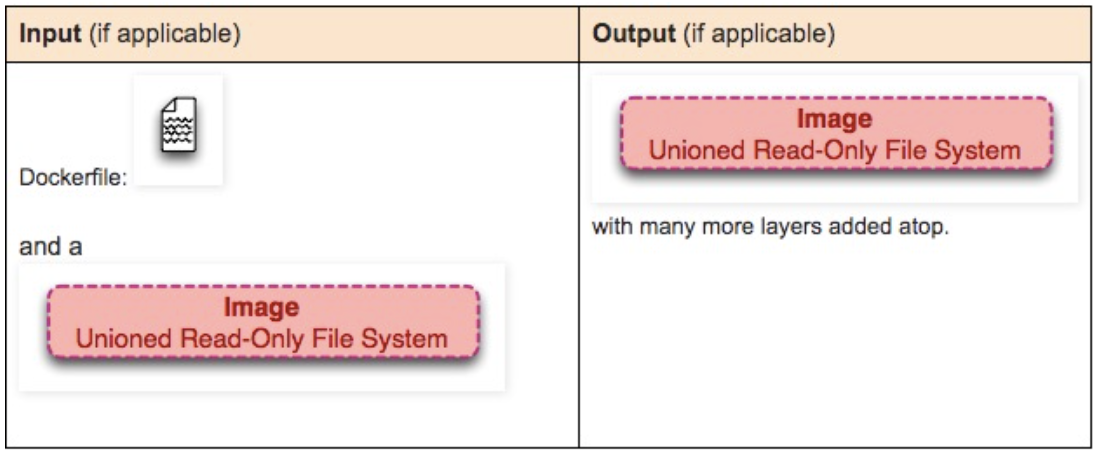
docker build
The build command gets the image from the FROM instruction in the Dockerfile, then repeatedly:
- run (create and start)
- modify
- commit
Each step in the loop generates a new layer, so many new layers are created.
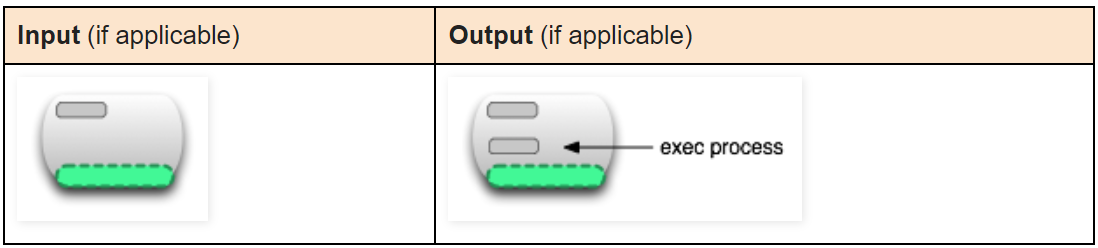
docker exec running-container-id
Execute a process in a running container
docker inspect container-id or image-id
Extract metadata from a container or image.

docker save image-id
Create a compressed file from the image. This compressed file preserves each layer and its metadata.
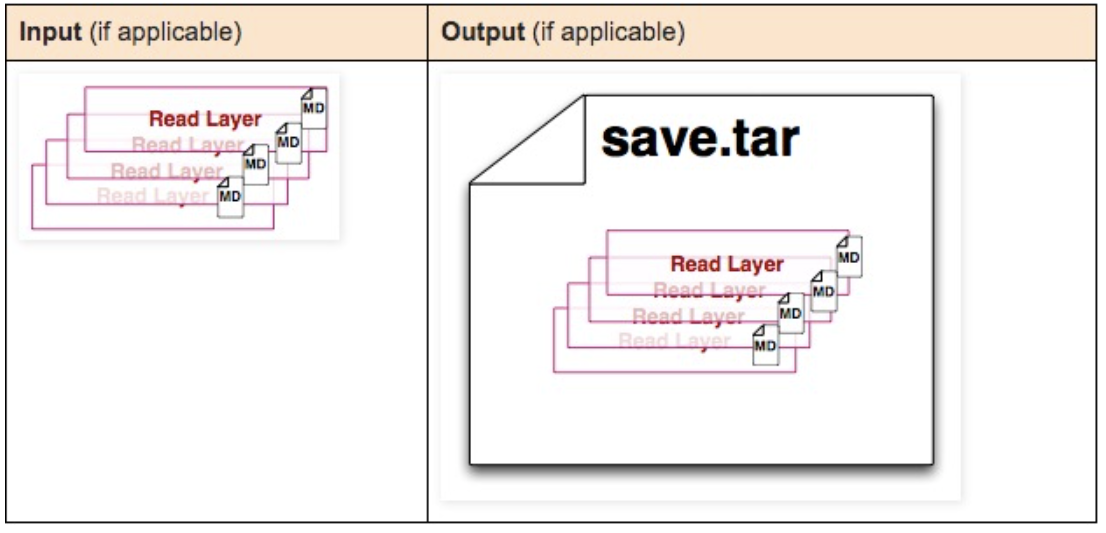
docker export container-id
Create a compressed file from the image. Compresses multiple image layers into one layer.
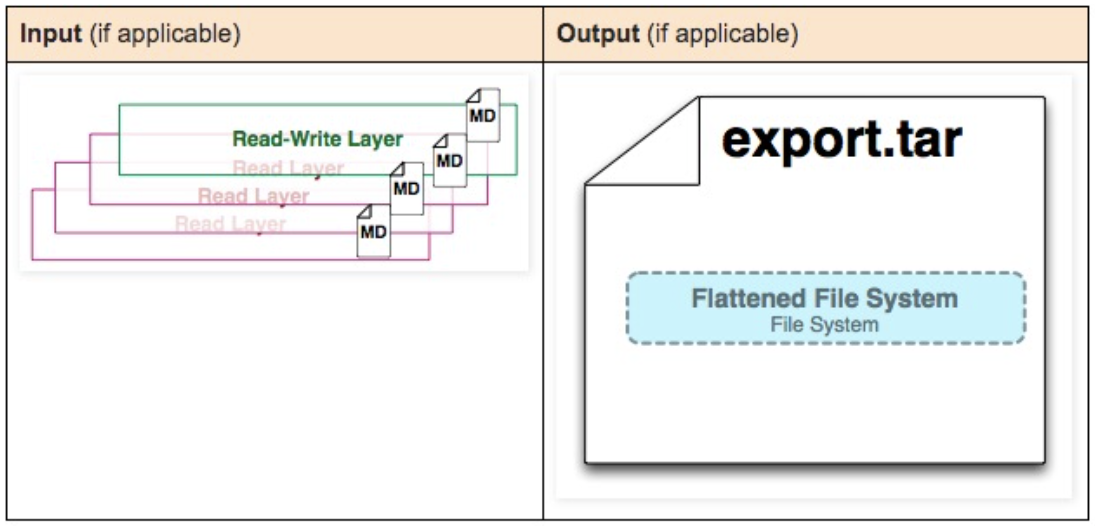
docker history image-id
View the creation history of the specified image.
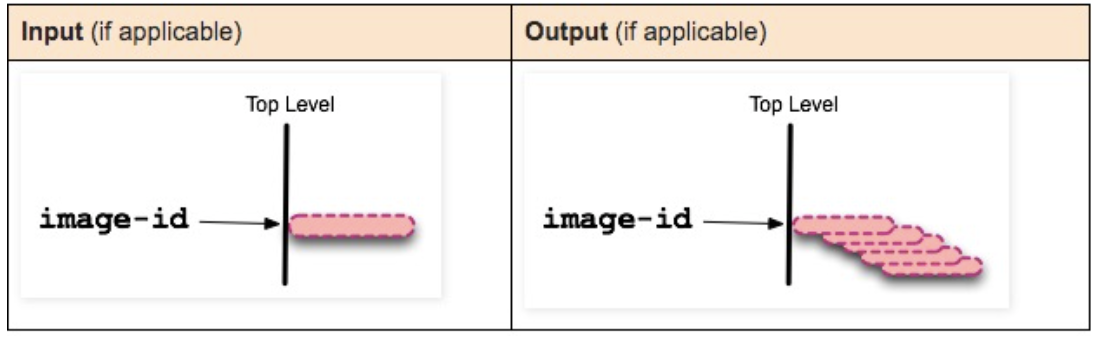
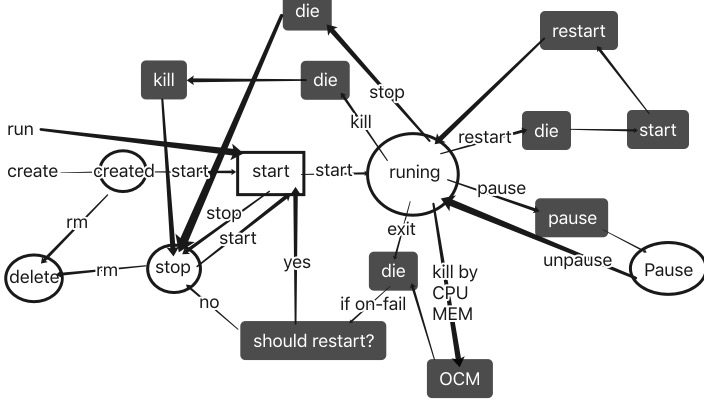
State Transitions